
Enable SSL, STARTTLS, and STLS
Click this check box to activate support for the SSL/TLS protocol and the STARTTLS and STLS extensions. Then, choose the certificate that you want to use from the list below.
Enable the dedicated SSL ports for SMTP, IMAP, POP3 servers
Enable this option if you want to make available the dedicated SSL ports specified on Ports under Default Domains & Servers. This will not affect clients using STARTTLS and STLS on the default mail ports — it merely provides an additional level of support for SSL.
SMTP server sends mail using STARTTLS when possible
Click this option if you want MDaemon to attempt to use the STARTTLS extension for every SMTP message it sends. If a server to which MDaemon is connecting doesn't support STARTTLS then the message will be delivered normally without using SSL. Use the STARTTLS White List if you wish to prevent the use of STARTTLS for certain domains.
SMTP server requires STARTTLS on MSA port
Enable this option if you wish to require STARTTLS for connections to the server made on the MSA port.
DomainPOP/MultiPOP servers use STLS whenever possible
Check this box if you want the DomainPOP and MultiPOP servers to use the STLS extension whenever possible.
Select certificate to use for SSL
This box displays your SSL certificates. Check the box next to any certificates you wish to be active. Click the star next to the one that you wish to set as the default certificate. MDaemon supports the Server Name Indication (SNI) extension to the TLS protocol, which allows a different certificate to be used for each of your server's host names. MDaemon will look at the active certificates and choose the one that has the requested host name in its Subject Alternative Names field (you can specify the alternate names when creating the certificate). If the client does not request a host name, or if no matching certificate is found, then the default certificate is used. Double-click a certificate to open it in Windows' Certificate dialog for review (only available in the application interface, not in the browser-based remote administration).
Delete
Select a certificate in the list and then click this button to delete it. A confirmation box will open and ask you if you are sure that you want to delete the certificate.
Create Certificate
Click this button to open the Create SSL Certificate dialog.
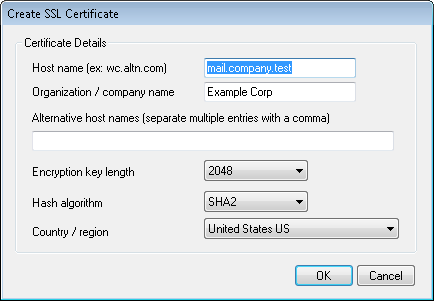
Certificate Details
Host name
When creating a certificate, enter the host name to which your users will connect (for example, "mail.example.com").
Organization/company name
Enter the organization or company that "owns" the certificate here.
Alternative host names (separate multiple entries with a comma)
If there are alternative host names to which users may be connecting and you want this certificate to apply to those names as well, then enter those domain names here separated by commas. Wildcards are permitted, so "*.example.com" would apply to all sub domains of example.com (for example, "wc.example.com", " mail.example.com", and so on).
|
MDaemon supports the Server Name Indication (SNI) extension to the TLS protocol, which allows a different certificate to be used for each of your server's host names. MDaemon will look at the active certificates and choose the one that has the requested host name in its Subject Alternative Names field. If the client does not request a host name, or if no matching certificate is found, then the default certificate is used. |
Encryption key length
Choose the desired bit-length of the encryption key for this certificate. The longer the encryption key the more secure the transferred data will be. Note, however, that not all applications support key lengths longer than 512.
Hash algorithm
Choose the hash algorithm that you wish to use: SHA1 or SHA2. The default setting is SHA2.
Country/region
Choose the country or region in which your server resides.
Restart servers
Click to restart the SMTP/IMAP/POP servers. The servers must be restarted when a certificate changes.
See:
Creating and Using SSL Certificates
